As the global climate crisis continues to evolve, the healthcare sector finds itself at a crossroads. The urgent need for more sustainable practices across industries has led to increased scrutiny of healthcare’s environmental footprint. Healthcare, while essential to public health, generates significant waste, uses massive amounts of resources, and produces harmful emissions. The world’s growing environmental challenges have pushed the healthcare sector to seek innovative, sustainable solutions to minimize its impact on the environment. Among these, sustainable nanomedicine has emerged as a revolutionary approach to healthcare that not only offers cutting-edge treatment solutions but also promises to reduce the environmental burden of medical practices.
The Climate Crisis and Healthcare’s Environmental Footprint
The healthcare industry is one of the largest contributors to global environmental issues. From the production of pharmaceuticals to the management of medical waste, healthcare activities are responsible for a considerable amount of pollution and resource consumption. In fact, studies have shown that the healthcare sector accounts for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, healthcare waste, particularly biomedical waste, is a growing concern, especially in developing countries like India. According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India generates approximately 774 tonnes of biomedical waste every day. While treatment facilities such as 208 operational Common Biomedical Waste Treatment Facilities (CBWTFs) and numerous captive treatment facilities have been set up, there are still major gaps in proper waste management, particularly in managing COVID-related waste. This significant waste generation, coupled with inadequate waste disposal practices in some regions, exacerbates the environmental impact of healthcare.
Read here CPCB Annual Report 2022- 23
The increasing generation of waste, including medical plastics, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, poses an immediate threat to both the environment and public health. The challenge now is to innovate within the healthcare sector to reduce these negative environmental effects, and sustainable nanomedicine presents a promising path forward.
What is Sustainable Nanomedicine?
Nanomedicine refers to the use of nanotechnology in the healthcare sector, particularly for diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases. Nanotechnology works by manipulating materials at the atomic or molecular scale, and when applied to medicine, it allows for precise drug delivery, improved diagnostics, and the development of advanced therapies. Sustainable nanomedicine is a subfield of this technology that integrates eco-friendly practices, focusing on reducing the environmental impact of medical treatments and waste.
Sustainable nanomedicine seeks to harness the power of nanotechnology to not only improve health outcomes but also create treatments that are both effective and environmentally sustainable. This involves using renewable resources, reducing the use of toxic chemicals, minimizing waste generation, and lowering the overall ecological footprint of medical procedures and drug manufacturing.
The benefits of sustainable nanomedicine are multifaceted. Firstly, it can reduce reliance on harmful synthetic drugs, which are often associated with toxic side effects and environmental pollution. Secondly, it enables the use of natural compounds in medical treatments, such as plant-based bioactive molecules, which can be encapsulated in nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. These practices not only enhance the effectiveness of treatments but also offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional synthetic drugs.
Sustainable Nanomedicine in Practice
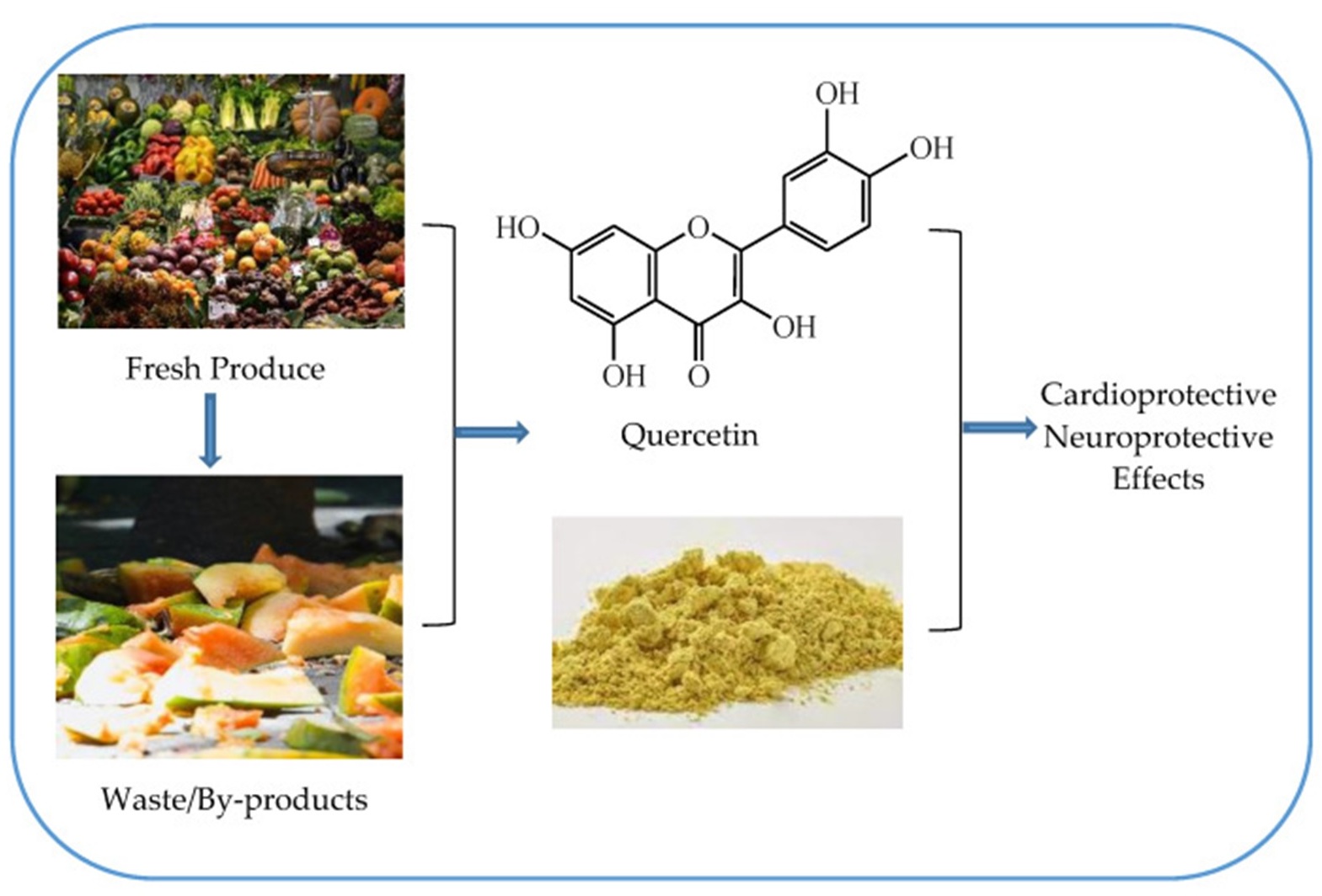 Recent advancements in sustainable nanomedicine have demonstrated the potential of this approach to revolutionize healthcare. One promising development is the use of natural bioactive compounds encapsulated in nanoparticles. These compounds, found in plants and other natural sources, have long been known for their therapeutic properties but are often difficult to deliver effectively due to low bioavailability and stability.
Recent advancements in sustainable nanomedicine have demonstrated the potential of this approach to revolutionize healthcare. One promising development is the use of natural bioactive compounds encapsulated in nanoparticles. These compounds, found in plants and other natural sources, have long been known for their therapeutic properties but are often difficult to deliver effectively due to low bioavailability and stability.
By using nanotechnology to encapsulate these compounds, researchers can enhance their bioavailability, stability, and solubility, making them more effective in treating a range of medical conditions. For example, quercetin, a bioactive compound found in plants such as Sambucus Canadensis, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, and antioxidant properties. When encapsulated in silver nanoparticles (QCT-AgNPs), quercetin becomes an effective treatment for diabetic wounds, a common complication of diabetes that can lead to amputations if untreated. The use of plant-based silver nanoparticles in this process not only offers an effective treatment option but also reduces the environmental toxicity often associated with the synthesis of synthetic nanomaterials.
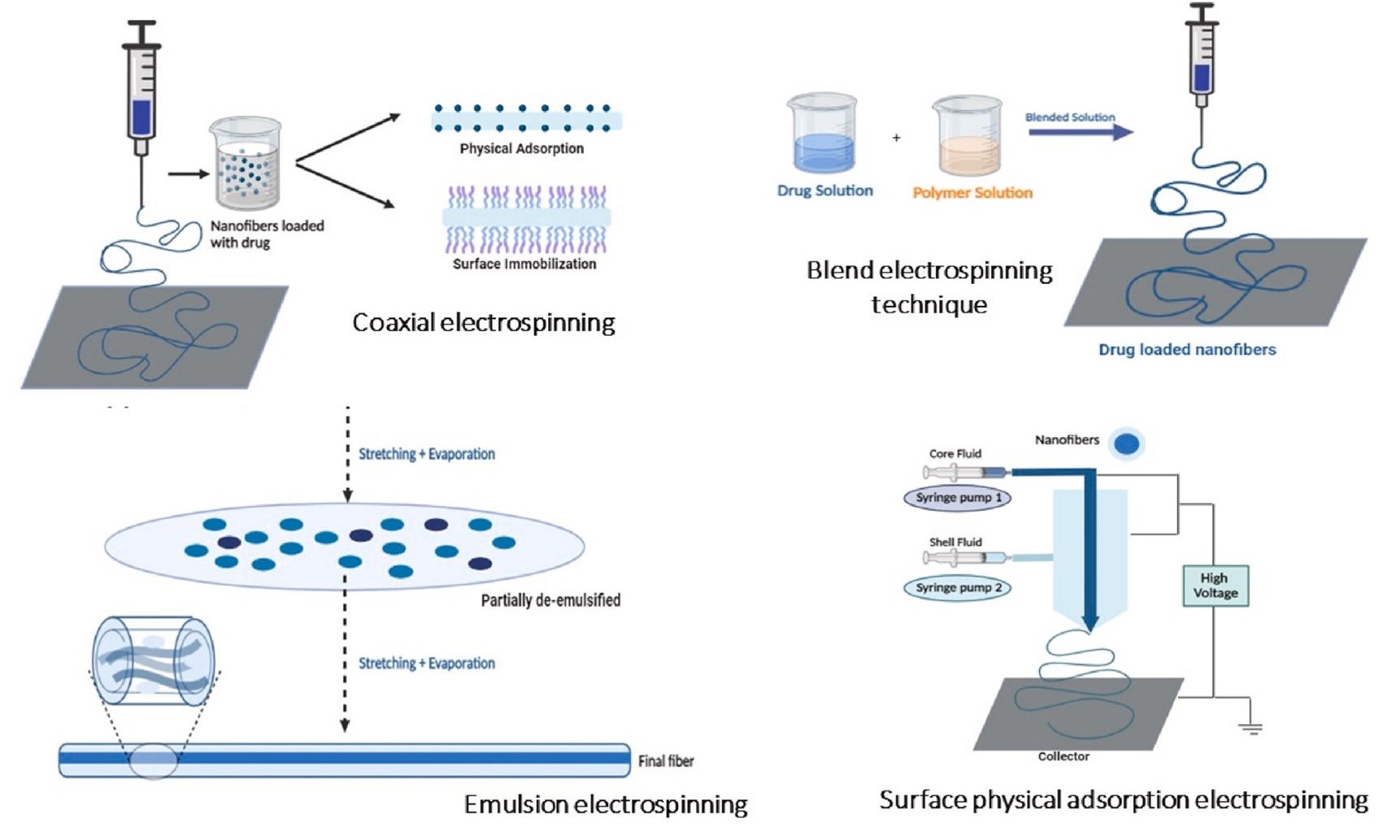
Another example of sustainable nanomedicine in practice is the development of electrospun nanofibers (ESNFs) made from plant mucilage. These nanofibers have been shown to support the proliferation of fibroblast cells, a critical component of wound healing. The use of plant-derived mucilage to create these nanofibers offers a non-toxic, environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic materials, reducing the ecological footprint of wound healing treatments.
These examples highlight the ability of sustainable nanomedicine to replace traditional, harmful medical practices with environmentally friendly alternatives, creating a healthcare system that benefits both patients and the planet.
 The Role of Plants in Sustainable Nanomedicine
The Role of Plants in Sustainable Nanomedicine
Plants play a pivotal role in the development of sustainable nanomedicine. Their use in synthesizing nano-formulations offers numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, non-toxicity, and eco-friendliness. Several plants contain natural compounds that can be used as reducing agents, stabilizers, and precursors in the synthesis of nanoparticles, eliminating the need for toxic chemicals typically used in traditional nanoparticle synthesis methods.
For instance, copper nanoparticles, which have been used for their antimicrobial properties, can be synthesized using plant extracts. This method is not only safer but also more environmentally sustainable compared to traditional methods that involve hazardous chemicals. The use of plant-based nanoparticles also reduces the environmental impact of nanoparticle synthesis, as the natural compounds in plants serve as both the reducing agents and stabilizers, making the process greener and more efficient.
In addition to their role in nanoparticle synthesis, plants also offer therapeutic properties that can be harnessed in sustainable nanomedicine. For example, compounds like flavonoids and alkaloids, which are abundant in plants, have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and antimicrobial properties. These plant-derived compounds can be used to develop sustainable treatments for a wide range of diseases, reducing the reliance on synthetic drugs that may have harmful environmental effects.
Challenges in Sustainable Nanomedicine
While the potential for sustainable nanomedicine is vast, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize its potential. One of the major hurdles is the synthesis of plant-based nanoparticles, which can be influenced by a variety of factors, including pH levels and temperature. These factors can affect the size, shape, and stability of nanoparticles, which in turn impacts their effectiveness as therapeutic agents.
Moreover, the environmental impact of nanoparticle synthesis and their disposal remains a concern. Nanomaterials can persist in the environment and potentially cause ecological harm. Some studies have raised concerns that the accumulation of nanomaterials in the environment could contribute to antibiotic resistance and harm plants and beneficial microorganisms. Therefore, comprehensive toxicological studies are essential to ensure that plant-based nanoparticles are safe for both humans and the environment.
Another challenge is the scalability of sustainable nanomedicine. While lab-scale production of plant-based nanoparticles has shown promise, scaling these processes for industrial production remains a complex task. This requires developing cost-effective and efficient methods for producing and purifying plant-based nanoparticles on a large scale.
The Future of Sustainable Nanomedicine
Despite these challenges, the future of sustainable nanomedicine looks promising. The growing emphasis on eco-friendly practices within the healthcare sector, combined with continued research and innovation in nanotechnology, will likely lead to the widespread adoption of sustainable nanomedicine in the coming years.
In particular, research is focusing on reducing the environmental impact of nanoparticle synthesis and ensuring their safety through toxicological testing. As the demand for sustainable healthcare solutions increases, it is expected that more funding and resources will be directed toward developing scalable methods for producing eco-friendly nanomedicine.
The use of plant-based nanoparticles could also become more prevalent as researchers continue to identify new plants with therapeutic properties. The ability to harness these plant compounds in an eco-friendly way offers exciting possibilities for the future of medicine, particularly in treating chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
Conclusion: Nanomedicine for a Greener Healthcare Future
In conclusion, sustainable nanomedicine represents a key innovation in the healthcare sector, offering the potential to transform both medical treatments and the environmental impact of the healthcare industry. By using plant-derived compounds and environmentally friendly nanoparticle synthesis techniques, sustainable nanomedicine provides an eco-conscious alternative to traditional medical practices.
As the world continues to face the dual challenges of climate change and rising healthcare costs, sustainable nanomedicine offers a pathway to more effective, affordable, and environmentally sustainable healthcare solutions. With continued research, investment, and collaboration, this revolutionary approach can shape a greener and healthier future for both patients and the planet.





 Recent advancements in sustainable nanomedicine have demonstrated the potential of this approach to revolutionize healthcare. One promising development is the use of natural bioactive compounds encapsulated in nanoparticles. These compounds, found in plants and other natural sources, have long been known for their therapeutic properties but are often difficult to deliver effectively due to low bioavailability and stability.
Recent advancements in sustainable nanomedicine have demonstrated the potential of this approach to revolutionize healthcare. One promising development is the use of natural bioactive compounds encapsulated in nanoparticles. These compounds, found in plants and other natural sources, have long been known for their therapeutic properties but are often difficult to deliver effectively due to low bioavailability and stability. The Role of Plants in Sustainable Nanomedicine
The Role of Plants in Sustainable Nanomedicine









