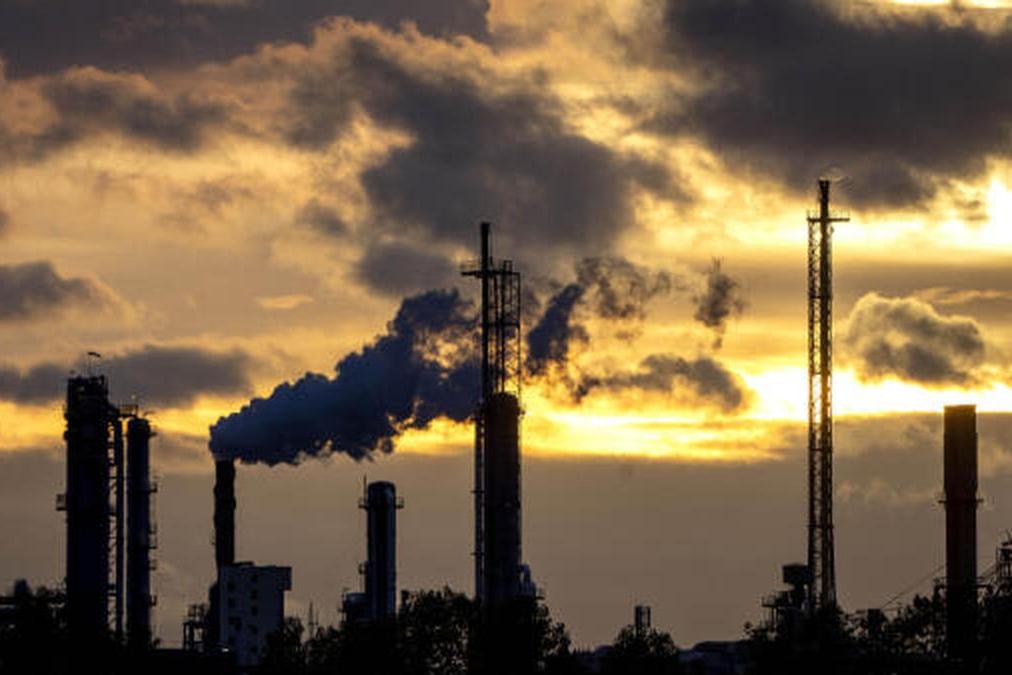
Do you know how essential greenhouse gases are for us to sustain on earth? During the day, the sun penetrates the atmosphere and ultimately heats the earth’s surface. At night, while the earth’s surface begins to cool down, it emits heat back into the atmosphere. This is the point where greenhouse gases stand at guard, playing a crucial role in trapping some of the heat in the atmosphere to maintain the earth's average temperature at around 14˚C (57˚F). As these gases have the ability to contain heat, they act as a glass shield, thereby playing a critical role in regulating the earth’s temperature and preventing some of the heat also called infrared radiations from escaping back into the space. A disturbance in the normal greenhouse gas activity could lead earth’s temperature to record a dip to as low as -18˚C (-0.4˚F).
Greenhouse gas effect
The natural process of these gases trapping the heat, maintaining earth’s temperature within a range that’s conducive to life and disallowing heat from entering back into the space is called greenhouse gas effect.
Types of greenhouse gases
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapourand various synthetic chemicals are the different kinds of greenhouse gases.
Carbon Dioxide- This gas is formed as a part of natural processes like volcanic eruption and respiratory mechanism of plants, animals and humans. However, increased human activities like burning fossil fuels, industrial revolution, deforestation, etc have added to carbon dioxide concentration over the years.
Methane- Another gas that’s produced naturally via the decomposition process wherein disintegration of organic complex matter into a simpler inorganic matter takes place. Wetlands and termite mounds are the natural sources of methane. Methane gas also comes from traditional ways of producing oil and gas, livestock farming, rice farming, landfill waste dumps, etc.
Nitrous Oxide- This greenhouse gas is produced during agricultural and industrial activities, fossil-fuel combustion, combustion of solid waste, use of commercial and agricultural fertilizers at a scale, during the production of nitric-acid and biomass burning.
Water Vapour- Water vapour is available in abundance, however, its life is too short. This form of greenhouse gas occurs naturally as a part of the global water cycle, and other human activities, but remains there just for a few days.
Synthetic Chemicals- Besides methane, Co2, nitrous oxide and water vapour, hydrofluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, perfluorocarbons, and other synthetic gases also carry the ability to consume or trap heat. However, these greenhouse gases are not produced naturally. They occur as a part of commercial, industrial and household usages. In other words, these are man-made gases.
What happens when greenhouse gas concentration increases?
With the ever-increasing levels of greenhouse gases, attributed mostly to human activities like burning of fossil fuels in cars, trains, planes, industrial set-up, deforestation, running of power plants, etc., excessive amounts of greenhouse gases are being added to the atmosphere. As the level of these gases increase, so does the earth’s temperature which is called global warming.
What will happen if global warming continues at this rate?
The rising global temperatures will have many adverse effects on every form of life at the earth. Seemingly, the biggest effect is the melting of glaciers and ice-bergs with an unprecedented speed. This will result in rising sea levels. As per scientists, the sea levels are risings by about 3.1 mm per year since 1993. Say, for instance, with the increase in global temperatures every year, all the available ice on this planet melts down, then the sea level will be up by 70 meters. Imagine a situation where many cities and parts of countries will be sub-merged in water. Millions of people will be displaced, irrigation and hydro-electric power generation will come to a halt. The ill-effects of global warming don’t stop here, seasons will also shift their course, rain and snow will take place an unexpected times, heat waves, jungle fires, and what not. In a nut shell, the global warming is the biggest threat to any form of life on this planet.
How to stop increasing levels of greenhouse gases?
There are two ways we can mitigate it- first, we have to stop adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and secondly, increasing the earth’s ability to pull these gases out of the atmosphere. This process is called climate mitigation.
Tips to reduce greenhouse gases:
- Adapt to and use more sustainable and alternative means of transportation that don’t use fossil fuels.
- Use public transport, carpooling; Develop a walking or cycling habit
- Using energy and electricity wisely and efficiently
- Reusing and recycling
- Eating less meat- Cows are known to produce methane in big amounts.
- Reforestation and planting trees- As trees absorb Co2, it helps in keeping the increased levels of carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere.