ESG scores have gained significant importance in today’s world, reflecting how companies are increasing their focus on sustainability and ethical practices. Simply put: ESG scores evaluate how companies manage their impact on the environment, social responsibilities, and governance structures. The rising awareness and importance of sustainability governance among corporates mean that ESG scores now play a vital role in their business strategy and investment decisions. So, high ESG scores show a strong commitment on the part of the company towards sustainability.
Let’s first understand the different components based on which ESG scores are calculated. We will then proceed to understand the process of calculating the scores themselves.
What Are ESG Scores: Components
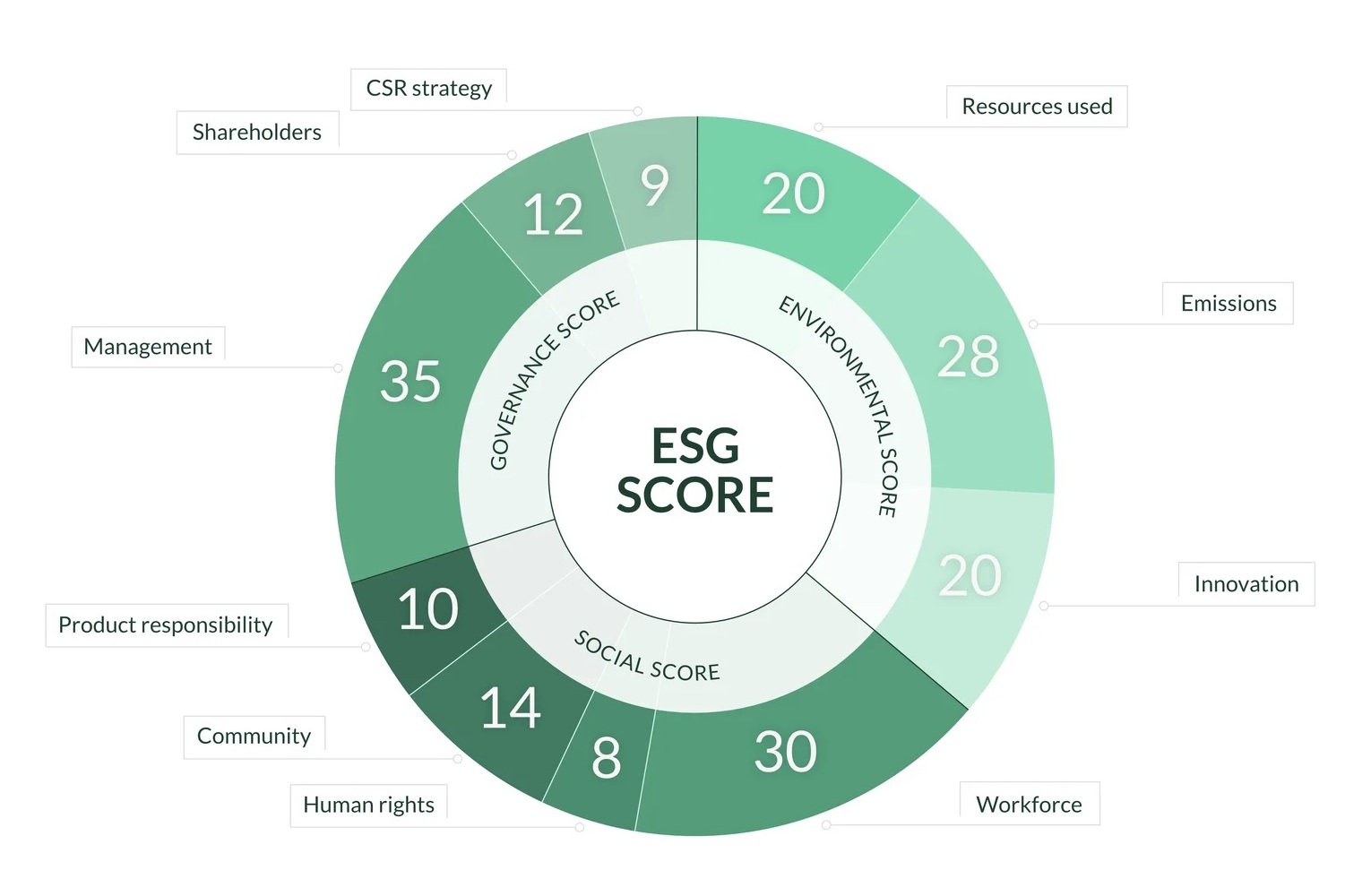
ESG scores evaluate a company’s performance in three critical areas: Environmental, Social, and Governance. Each component helps us understand how any particular company measures up in its sustainability and ethical practices.
Environmental
The Environmental component focuses on how a company interacts with the natural world. Key factors include:
- Climate Change and Carbon Emissions: This examines how companies address climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
- Resource Depletion and Pollution: This includes practices to reduce waste, manage water usage, and prevent contamination of soil and water.
- Biodiversity and Conservation: This evaluates efforts to preserve natural habitats and biodiversity. Companies that participate in conservation projects and take measures to protect ecosystems score well in this area
Social
The Social component focuses on a company’s relationships with its employees, customers, and communities. Key factors include:
- Human Rights and Labour Practices: This examines the organisation’s attitude towards human rights. It includes policies against forced and child labour, fair wages, and safe working conditions.
- Welfare and Diversity of Employees: This assesses how companies support the well-being of their employees and promote diversity and inclusion. It covers benefits, opportunities for growth, and the measures it takes to ensure a diverse and inclusive workplace.
- Community Engagement: This looks at how companies interact with and contribute to their local communities including community development projects, and charitable contributions.
Governance
The Governance component evaluates the systems and processes a company uses to manage itself. Key factors include:
- Board Structure and Independence: This examines the composition and independence of the company’s board of directors. A diverse and independent board is seen as more capable of making effective decisions.
- Executive Compensation and Accountability: This component assesses how companies compensate their executives and if the compensations are transparent and fair.
- Shareholder Rights: This looks at how companies uphold shareholder rights and maintain transparency in their operations.
Why Are ESG Scores Important
ESG scores play a crucial role in today’s business landscape and impacting various stakeholders of a company, including investors, companies, and consumers.
- How Does it Help Investors: ESG scores have become a vital tool for investors seeking to make informed decisions about potential investments. A high ESG score indicates that a company manages its environmental, social, and governance risks effectively. Investors often look for companies with strong ESG performance because they are seen as more resilient and better managed. This translates to lower risks and potentially higher returns over the long term. Many investors now integrate ESG criteria into their investment strategies to align with their values and mitigate risks associated with poor sustainability practices.
- How Does it Help Companies: Companies benefit significantly from achieving high ESG scores. These scores enhance their reputation and attract investors who prioritise sustainability. A strong ESG performance can lead to a competitive advantage, as consumers and business partners increasingly prefer to engage with companies that demonstrate responsible practices.High ESG scores can also help companies identify areas for improvement through regular assessments. This proactive approach not only boosts a company’s ESG score but also drives innovation and operational efficiency.
- How Does it Help Consumers: Consumers today are more conscious of the impact of their purchasing decisions. High ESG scores provide assurance that a company adheres to ethical and sustainable practices. This transparency helps consumers make choices that align with their values, supporting businesses that contribute positively to society and the environment.
How Are ESG Scores Calculated
ESG scores are complex metrics derived by combining methods of data collection, analysis, and assessment methodologies.
- Data Collection: The calculation of ESG scores starts with data collection. Rating agencies gather information from a variety of sources, including company reports, regulatory filings, and third-party data providers. Publicly available data, such as sustainability reports and disclosures, play a significant role. In India, most companies use the SEBI-introducedBusiness Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) disclosure format to create ESG reports. This data covers a wide range of topics, from greenhouse gas emissions to labour practices and corporate governance structures.Agencies also use data from news articles, academic research, and governmental databases. This broad spectrum of sources ensures that they have a comprehensive view of the organisation’s activities and their impact on ESG factors.
- Analysis and Weighting: Once the data is collected, it undergoes rigorous analysis. ESG rating agencies use proprietary methodologies to evaluate the information. Each factor within the E,S, and G categories receives a specific weight based on its importance and relevance to the industry. For example, carbon emissions might carry more weight for a manufacturing company than for a financial services firm.The analysis often involves assessing hundreds of metrics. Many agencies evaluate aspects such as energy efficiency, water usage, human rights practices, board diversity, and executive compensation.Each of these factors is scored, and the scores are then aggregated into the three main ESG categories. The final ESG score represents a weighted average of these individual scores, reflecting the company’s overall performance in managing its environmental, social, and governance responsibilities.
- Peer Comparison and Benchmarking: ESG scores are also relative, meaning they compare a company’s performance to its peers within the same industry. This peer comparison helps investors understand how a company stands relative to others in similar fields. Companies are scored on a scale, which could be numerical (e.g., 0 to 100) or categorical (e.g., AAA to CCC). This benchmarking makes it easier to see where a company excels or needs improvement.
- Verification and Quality Control: To ensure accuracy and reliability, ESG rating agencies implement robust verification processes. They cross-check data against multiple sources and may conduct interviews with company management. This step is crucial for identifying discrepancies and validating the information used in the scoring process.Agencies also engage in continuous monitoring to update scores as new data becomes available. This dynamic aspect of ESG scoring means that scores can change over time with a company’s efforts and developments in ESG areas.
Some Global and Indian ESG Ratings Providers
|
Provider
|
Region
|
Rating Scale
|
|
MSCI
|
Global
|
AAA to CCC
|
|
S&P Global
|
Global
|
0 to 100
|
|
ISS ESG
|
Global
|
1 to 10
|
|
CRISIL ESG Ratings & Analytics
|
India
|
0 to 100
|
|
CARE ESG Ratings Limited
|
India
|
ESG 1 to ESG 4 (1 being the highest)
|
|
ESG Risk Assessments & Insights
|
India
|
ESG 0 to ESG 4 (4 being the highest)
|
|
IIAS Sustainability Solutions
|
India
|
Customised Ratings (NA)
|
|
SES ESG Research Private Limited
|
India
|
Customised Ratings (NA)
|
|
Pragati Development Consulting
|
India
|
Customised Ratings (NA)
|
|
PGS Impact Private Limited
|
India
|
Customised Ratings (NA)
|