 In the era of technological advancement, Digital Inclusion has become a fundamental necessity, ensuring that individuals, regardless of their background or location, can access and leverage computer and internet technologies. While India has made significant strides in terms of digital access in the past few years, there is still a lot more to be done. Oxfam’s India Inequality Report 2022 points out towards the digital divide that continues to exist in the country. Citing many statistics indicating the existing inequality in access (e.g. of all the students enrolled in any course, only 25% had access to the internet through any device and only 9% had that access through a computer). The report highlights economic inequality as the key driver of this divide and suggests ensuring availability and affordability as the most basic steps to bridge it.
In the era of technological advancement, Digital Inclusion has become a fundamental necessity, ensuring that individuals, regardless of their background or location, can access and leverage computer and internet technologies. While India has made significant strides in terms of digital access in the past few years, there is still a lot more to be done. Oxfam’s India Inequality Report 2022 points out towards the digital divide that continues to exist in the country. Citing many statistics indicating the existing inequality in access (e.g. of all the students enrolled in any course, only 25% had access to the internet through any device and only 9% had that access through a computer). The report highlights economic inequality as the key driver of this divide and suggests ensuring availability and affordability as the most basic steps to bridge it.
In this article, Ms. Anju Kanodia, Executive Director, Lumina Datamatics, delves into the persistent digital divide in India, where a substantial portion of the population lacks access to crucial digital resources. Despite the transformative potential of digital technologies in areas like education and healthcare, the existing gap perpetuates inequality, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. Recognizing the imperative of addressing this disparity, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives are emerging as pivotal players in bridging the digital gap. This article explores the multifaceted role of CSR in fostering digital inclusion, from infrastructure development to skills enhancement programs, emphasizing the collective responsibility of public, private, and civil society organizations in realizing a digitally inclusive and sustainable future for India.
Scroll down to read the full article:
Digital Inclusion refers to the phenomenon where people, regardless of their background or location, can access and utilize computer and internet technologies. It is a crucial aspect of modern-day life, as digital technologies have become integral to people's lives in essential activities such as education, healthcare, and business. However, in India, the digital divide remains a significant challenge, hindering digital inclusion. Consequently, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives are becoming increasingly important to bridge the digital divide and promote digital inclusion in India.
The Digital Divide in India:
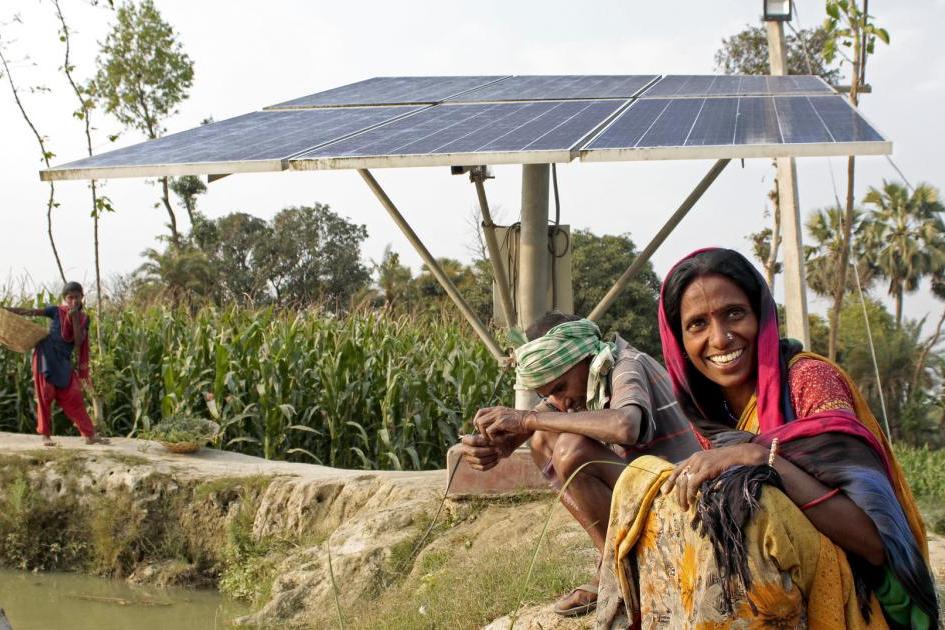
The digital divide in India refers to the gap between people who have access to digital technologies, such as computers and the internet, and those who do not. It is a significant concern, as it affects people's opportunities and potential. The digital divide has severe implications for inequality in India. As digital technologies become more ubiquitous, the lack of digital inclusion perpetuates an unequal opportunity structure, further aggravating the economic and social disparities. For instance, the digital divide disproportionately affects marginalized communities such as women, ethnic minorities, and people living in remote rural areas, who face an unequal distribution of resources to access digital technologies. This leads to unequal economic gains and limited access to essential services like healthcare and education, thereby contributing to the widening socio-economic gap.
Bridging the Digital Divide in India through CSR:
The digital divide is a pressing issue that requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders. CSR initiatives can play a significant role in bridging the digital divide and promoting digital inclusion in India. Some of the possible strategies that CSR initiatives can focus on include:
- Digital Infrastructure Development: CSR initiatives can focus on investing in infrastructure development, such as building internet connectivity, setting up computer labs and providing necessary support for digital learning centers in rural areas.
- Digital Skills Development Programs: Launching digital literacy programs is essential for empowering individuals with the skills needed to navigate the digital landscape. CSR funds can be utilized to conduct workshops, training sessions, and awareness programs to enhance digital literacy among various demographic groups.
- Supporting Educational Institutions: CSR initiatives can be directed towards supporting educational institutions in adopting digital learning technologies. This includes providing schools with the necessary hardware, software, and training for teachers to integrate technology into the curriculum effectively.
- Localized Content for Regional Languages: Language diversity is a unique challenge in India. CSR initiatives can promote and create digital content in regional languages to cater to diverse linguistic communities. This would encourage information access, digital literacy, and content consumption.
Conclusion:
Bridging the digital divide in India requires collective efforts from public, private, and civil society organizations. By integrating digital inclusion strategies into their CSR initiatives, companies can contribute to building a digitally included society and unlock new possibilities for underprivileged communities. These efforts can create positive impacts in reducing inequality, promoting economic growth, and enhancing opportunities for all Indians, irrespective of their location or socio-economic background. Together, we can bridge the digital divide and accelerate India's journey towards digital inclusion and sustainable development.




 In the era of technological advancement, Digital Inclusion has become a fundamental necessity, ensuring that individuals, regardless of their background or location, can access and leverage computer and internet technologies. While India has made significant strides in terms of digital access in the past few years, there is still a lot more to be done. Oxfam’s India Inequality Report 2022 points out towards the digital divide that continues to exist in the country. Citing many statistics indicating the existing inequality in access (e.g. of all the students enrolled in any course, only 25% had access to the internet through any device and only 9% had that access through a computer). The report highlights economic inequality as the key driver of this divide and suggests ensuring availability and affordability as the most basic steps to bridge it.
In the era of technological advancement, Digital Inclusion has become a fundamental necessity, ensuring that individuals, regardless of their background or location, can access and leverage computer and internet technologies. While India has made significant strides in terms of digital access in the past few years, there is still a lot more to be done. Oxfam’s India Inequality Report 2022 points out towards the digital divide that continues to exist in the country. Citing many statistics indicating the existing inequality in access (e.g. of all the students enrolled in any course, only 25% had access to the internet through any device and only 9% had that access through a computer). The report highlights economic inequality as the key driver of this divide and suggests ensuring availability and affordability as the most basic steps to bridge it.


.jpg)










